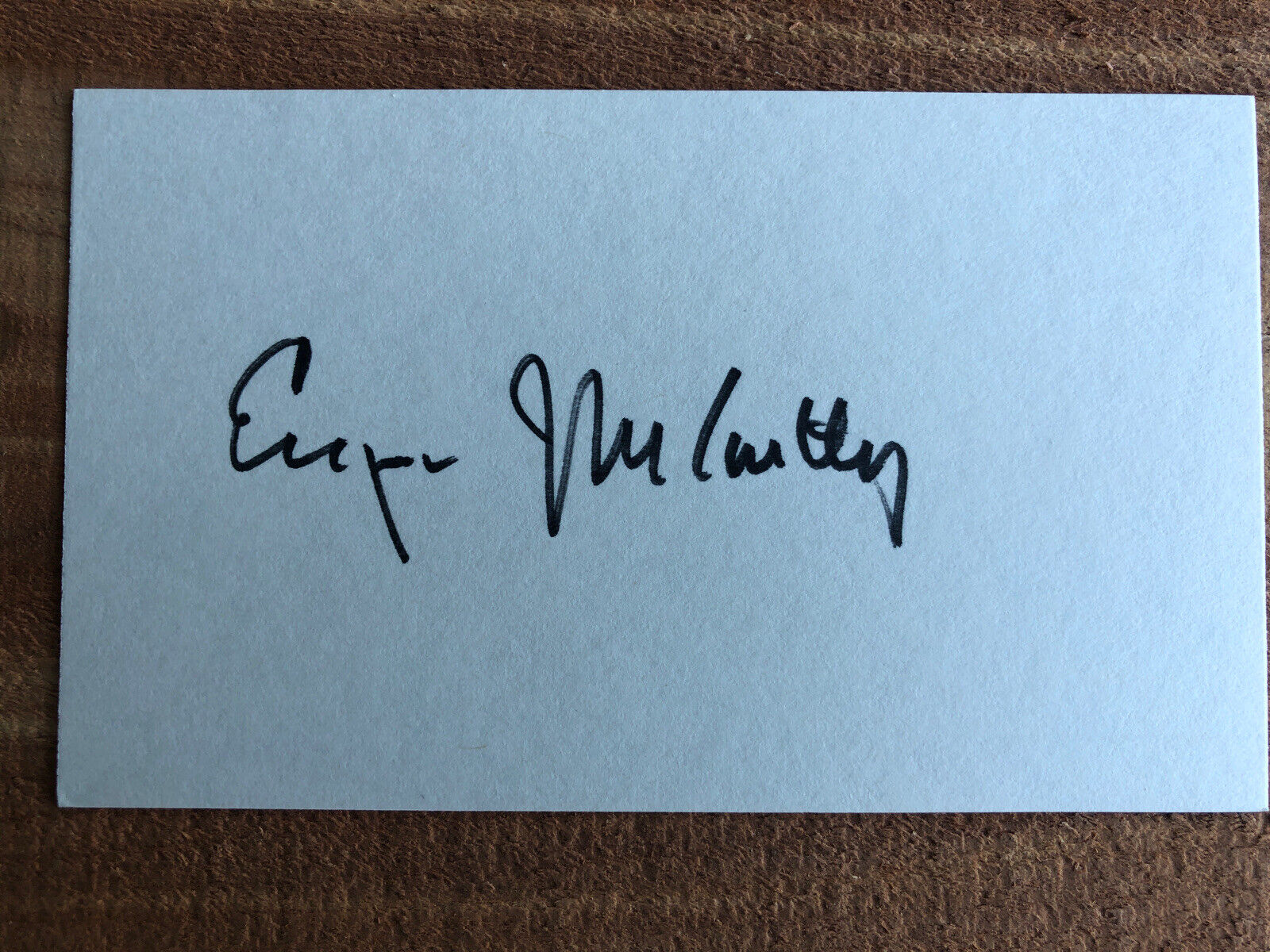-40%
autograph Union Senator Charles Sumner of Massachusetts
$ 26.4
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Condition as seen. Size 4 by 1 inch, "Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner - Brady-Handy.jpg
Sumner, c. 1860s
United States Senator
from Massachusetts
In office
April 24, 1851 – March 11, 1874
Preceded by
Robert Rantoul Jr.
Succeeded by
William B. Washburn
Chair of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee
In office
March 4, 1861 – March 4, 1871
Preceded by
James M. Mason
Succeeded by
Simon Cameron
Personal details
Born
January 6, 1811
Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.
Died
March 11, 1874 (aged 63)
Washington D.C, U.S.
Resting place
Mount Auburn Cemetery
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Political party
Whig (1840–1848)
Free Soil (1848–1854)
Republican (1854–1870)
Liberal Republican (1870–1872)
Spouse(s)
Alice Hooper
(m. 1866; div. 1873)
Education
Boston Latin School
Alma mater
Harvard University
Profession
Politician
Signature
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811 – March 11, 1874) was an American politician and United States Senator from Massachusetts. As an academic lawyer and a powerful orator, Sumner was the leader of the anti-slavery forces in Massachusetts and a leader of the Radical Republicans in the U.S. Senate during the American Civil War. He worked hard to destroy the Confederacy, free all the slaves, and keep on good terms with Europe. During Reconstruction, he fought to minimize the power of the ex-Confederates and guarantee equal rights to the freedmen. He fell into a dispute with fellow Republican President Ulysses Grant on the question of taking control of Santo Domingo. Grant's allies stripped Sumner of his power in the Senate in 1871, and he joined the Liberal Republican movement in an effort to defeat Grant's reelection in 1872.
Sumner changed his political party several times as anti-slavery coalitions rose and fell in the 1830s and 1840s before coalescing in the 1850s as the Republican Party, the affiliation with which he became best known. He devoted his enormous energies to the destruction of what Republicans called the Slave Power, the influence over the federal government of Southern slave owners who sought the continuation and expansion of slavery.[1] In 1856, a South Carolina Congressman, Democrat Preston Brooks, nearly killed Sumner on the Senate floor two days after Sumner delivered an intensely anti-slavery speech called "The Crime Against Kansas."[2] In the speech, Sumner characterized the attacker's cousin,[3][4] South Carolina Senator Andrew Butler, a Democrat, as a pimp for slavery.[5] The episode played a major role in the coming of the Civil War. During the war, Sumner was a leader of the Radical Republican faction that criticized President Abraham Lincoln for being too moderate on the South. One of the most learned statesmen of the era, he specialized in foreign affairs, and worked closely with Abraham Lincoln to keep the British and the French from intervening on the side of the Confederacy during the Civil War. Sumner's expertise and energy made him a powerful chairman of the Senate Committee on Foreign Relations.
As the chief Radical leader in the Senate during Reconstruction, Sumner fought hard to provide equal civil and voting rights for the freedmen on the grounds that "consent of the governed" was a basic principle of American republicanism, and to block ex-Confederates from power so they would not reverse the gains made from the Union's victory in the Civil War. Sumner, teaming with House leader Thaddeus Stevens, battled Andrew Johnson's reconstruction plans and sought to impose a Radical program on the South. Although Sumner forcefully advocated the annexation of Alaska in the Senate, he was against the annexation of the Dominican Republic, then known by the name of its capital, Santo Domingo. After leading Senators to defeat President Ulysses S. Grant's Santo Domingo Treaty in 1870, Sumner broke with Grant, and denounced him in such terms that reconciliation was impossible. In 1871, President Grant and his Secretary of State Hamilton Fish retaliated; through Grant's supporters in the Senate, Sumner was deposed as head of the Foreign Relations Committee. Sumner had become convinced that Grant was a corrupt despot and that the success of Reconstruction policies called for new national leadership. Sumner bitterly opposed Grant's reelection by supporting the Liberal Republican candidate Horace Greeley in 1872 and lost his power inside the Republican Party. Less than two years later, he died in office."